Archive for the ‘cosmology’ category: Page 373
Jan 25, 2018
Bioquark Inc. — Best Damn Podcast — Ira Pastor
Posted by Ira S. Pastor in categories: aging, bioengineering, business, cosmology, cryonics, DNA, futurism, genetics, health, life extension
Jan 22, 2018
Bioquark Inc. — The Richard Syrett Show — Ira Pastor — Bioregeneration
Posted by Ira S. Pastor in categories: aging, bioengineering, biotech/medical, bitcoin, cosmology, cryonics, disruptive technology, DNA, futurism, health
Jan 21, 2018
Bioquark Inc. — The Edge News Television — Ira Pastor
Posted by Ira S. Pastor in categories: aging, alien life, bioengineering, biotech/medical, cosmology, DNA, futurism, genetics, geopolitics, life extension
Jan 10, 2018
A New Hypothesis Suggests That Parallel Universes Might Interact after All
Posted by Shailesh Prasad in categories: cosmology, quantum physics
A new conception of quantum mechanics rests on the idea that parallel universes exist, and that they interact with our own to create weird and wonderful quantum phenomena.
Jan 9, 2018
Bioquark Inc. — Ira Pastor — X-Zone Radio Show
Posted by Ira S. Pastor in categories: aging, bioengineering, biotech/medical, cosmology, cryonics, DNA, futurism, genetics, life extension, transhumanism
Jan 8, 2018
Bioquark Inc. — At The End of the Day Show
Posted by Ira S. Pastor in categories: aging, bioengineering, biotech/medical, business, cosmology, cryonics, DNA, futurism, genetics, transhumanism
Jan 7, 2018
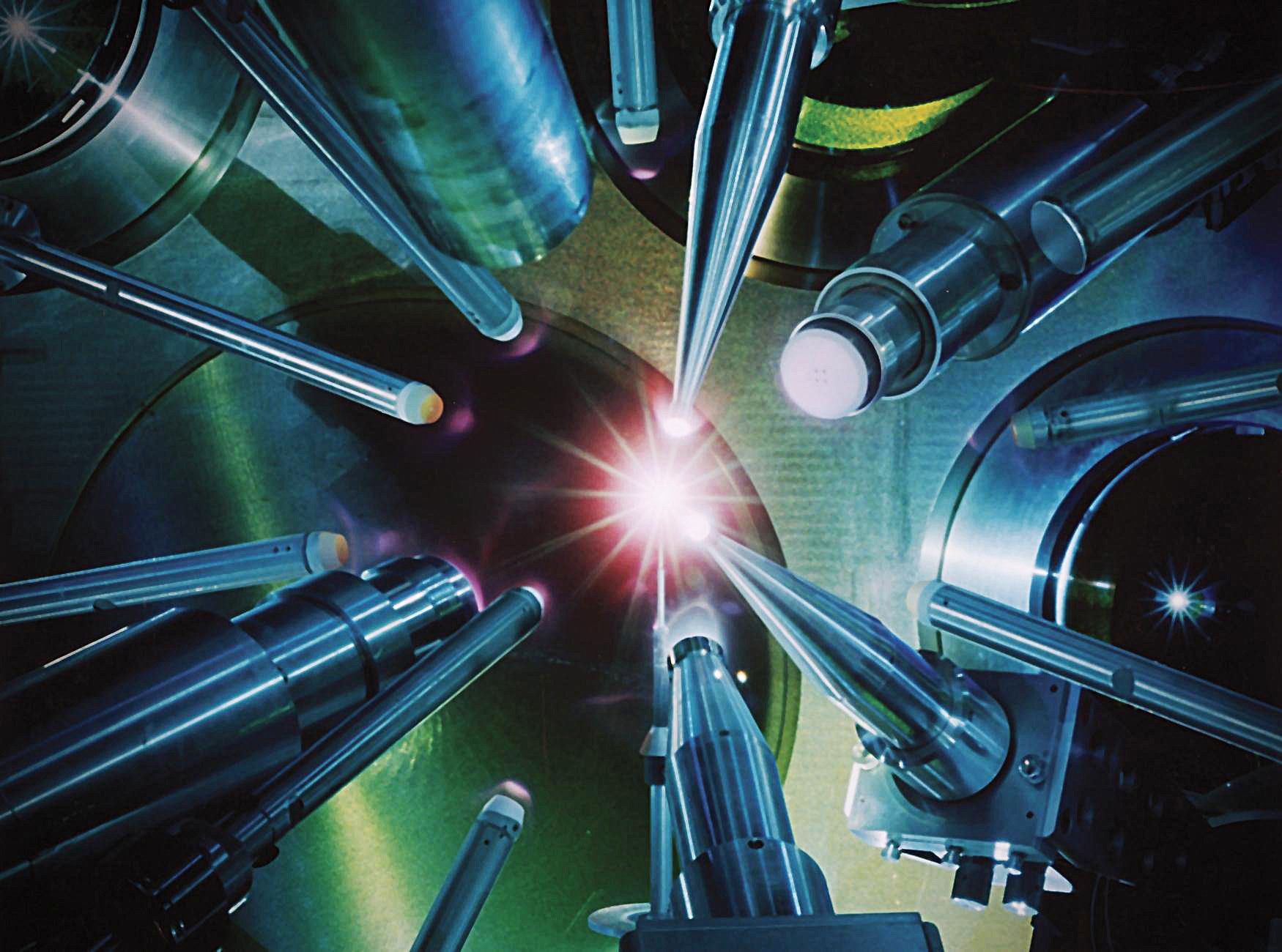
Computational astrophysics team uncloaks magnetic fields of cosmic events
Posted by Shailesh Prasad in categories: computing, cosmology, physics
The development of ultra-intense lasers delivering the same power as the entire U.S. power grid has enabled the study of cosmic phenomena such as supernovae and black holes in earthbound laboratories. Now, a new method developed by computational astrophysicists at the University of Chicago allows scientists to analyze a key characteristic of these events: their powerful and complex magnetic fields.
In the field of high-energy density physics, or HEDP, scientists study a wide range of astrophysical objects—stars, supermassive black holes at the center of galaxies and galaxy clusters—with laboratory experiments as small as a penny and lasting only a few billionths of a second. By focusing powerful lasers on a carefully designed target, researchers can produce plasmas that reproduce conditions observed by astronomers in our sun and distant galaxies.
Planning these complex and expensive experiments requires large-scale, high-fidelity computer simulation beforehand. Since 2012, the Flash Center for Computational Science of the Department of Astronomy & Astrophysics at UChicago has provided the leading open computer code, called FLASH, for these HEDP simulations, enabling researchers to fine-tune experiments and develop analysis methods before execution at sites such as the National Ignition Facility at Lawrence Livermore National Laboratory or the OMEGA Laser Facility in Rochester, N.Y.
Continue reading “Computational astrophysics team uncloaks magnetic fields of cosmic events” »