Nov 29, 2020
A new way to map out dark matter is 10 times more precise than the previous-best method
Posted by Quinn Sena in categories: cosmology, physics
Astronomers have to be extra clever to map out the invisible dark matter in the universe. Recently, a team of researchers have improved an existing technique, making it up to ten times better at seeing in the dark.
Dark matter is frustratingly difficult to measure. It’s completely invisible: it simply doesn’t interact with light (or normal matter) in any way, shape, or form. But we know that dark matter exists because of its gravitational influence on everything around it – including the normal matter that makes up stars and galaxies.
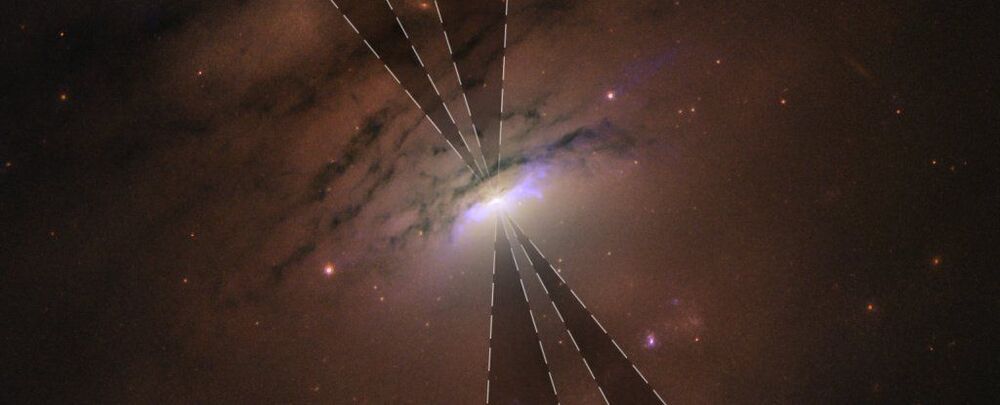
As an example of this, take a look at gravitational lensing. A massive object, whether made of dark or normal matter, will bend the path of any light that passes close by. It’s usually an incredibly tiny effect, but definitely measurable. We can see lensing of starlight around the sun, for example, which is how we knew that Einstein’s theory of general relativity must be correct.