Oct 19, 2024
Black Holes Could Be Back Doors to Other Universes, Scientist Claims
Posted by Shubham Ghosh Roy in categories: cosmology, physics, singularity
SCATTERED THROUGHOUT THE UNIVERSE are ravenous black holes that pull gas, dust, light and even other black holes into their maw, never to be seen again. Like a riptide pulling swimmers out to sea, the gravity inside a black hole pulls matter past a point of no return, called the event horizon, and condenses it so tightly that physics as we know it begins to break down, creating a “singularity.” It’s this singularity, in particular, that troubles physicists because it throws their most important theories about the universe into question.
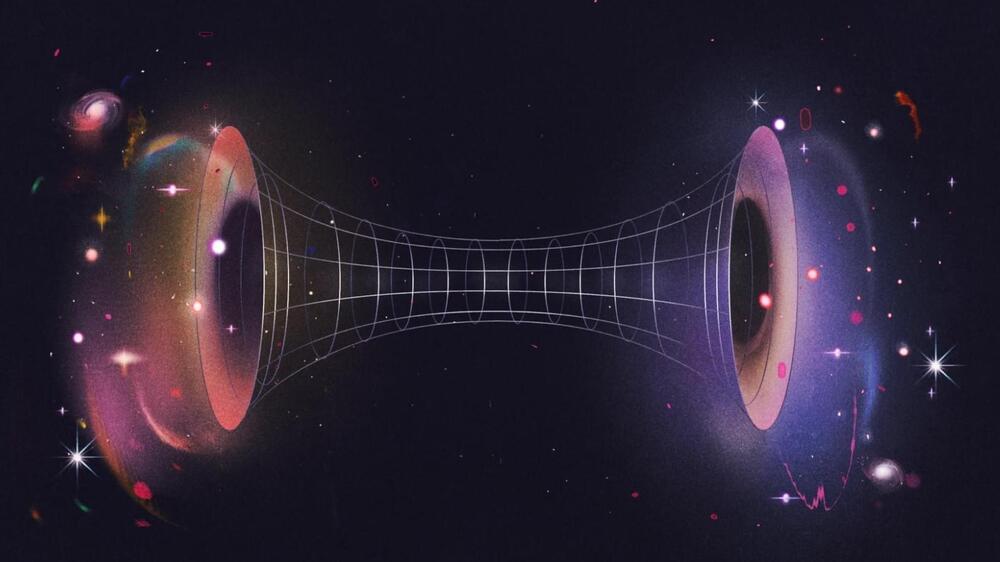
That’s why theoretical physicist Nikodem Poplawski, Ph.D., asked a big question back in 2010: what if black holes don’t contain a singularity at all? Instead, Poplawski’s theory suggests, the center of a black hole could contain a pathway into another universe. Weirder yet, his theory predicts that this may be how our own universe was created.
A paper describing this work, titled “Radial motion into an Einstein–Rosen bridge,” was published 14 years ago in the journal Physics Letters B. While the theory captured attention at the time, this topic is still rather niche among physicists. Many researchers have either moved on, or have never heard of the idea to begin with.