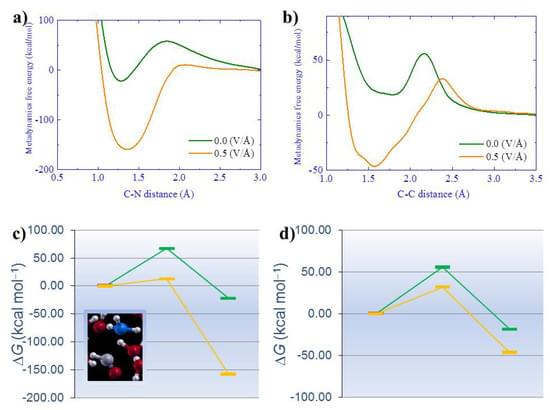
Hoping to improve on those earlier efforts, Matthew Daugherty, a biochemist at the University of California San Diego, and colleagues used sophisticated computer software to trace the evolution of hundreds of human genes by searching for similar sequences in hundreds of other species. Genes that seemed to have appeared first in vertebrates and had no predecessors in earlier animals were good candidates for having jumped across from bacteria, particularly if they had counterparts in modern microbes. Among the dozens of potentially alien genes, one “blew me away,” Daugherty recalls.
The gene, called IRBP (for interphotoreceptor retinoid-binding protein), was already known to be important for seeing. The protein it encodes resides in the space between the retina and the retinal pigment epithelium, a thin layer of cells overlying the retina. In the vertebrate eye, when light hits a light-sensitive photoreceptor in the retina, vitamin A complexes become kinked, setting off an electrical pulse that activates the optic nerve. IRBP then shifts these molecules to the epithelium to be unkinked. Finally, it shuttles the restored molecules back to the photoreceptor. “IRBP,” Zhu explains, “is essential for the vision of all vertebrates.”
Vertebrate IRBP most closely resembles a class of bacterial genes called pepsidases, whose proteins recycle other proteins. Since IRBP is found in all vertebrates but generally not in their closest invertebrate relatives, Daugherty and his colleagues propose that more than 500 million years ago microbes transferred a pepsidase gene into an ancestor of all living vertebrates. Once the gene was in place, the protein’s recycling function was lost and the gene duplicated itself twice, explaining why IRBP has four copies of the original pepsidase DNA. Even in its microbial forebears, this protein may have had some ability to bind to light-sensing molecules, Daugherty suggests. Other mutations then completed its transformation into a molecule that could escape from cells and serve as a shuttle.