Aug 14, 2015
First 3D-Printed Drug Ushers in Era of Downloadable Medicine — Singularity HUB
Posted by Shailesh Prasad in categories: 3D printing, biotech/medical, neuroscience, singularity
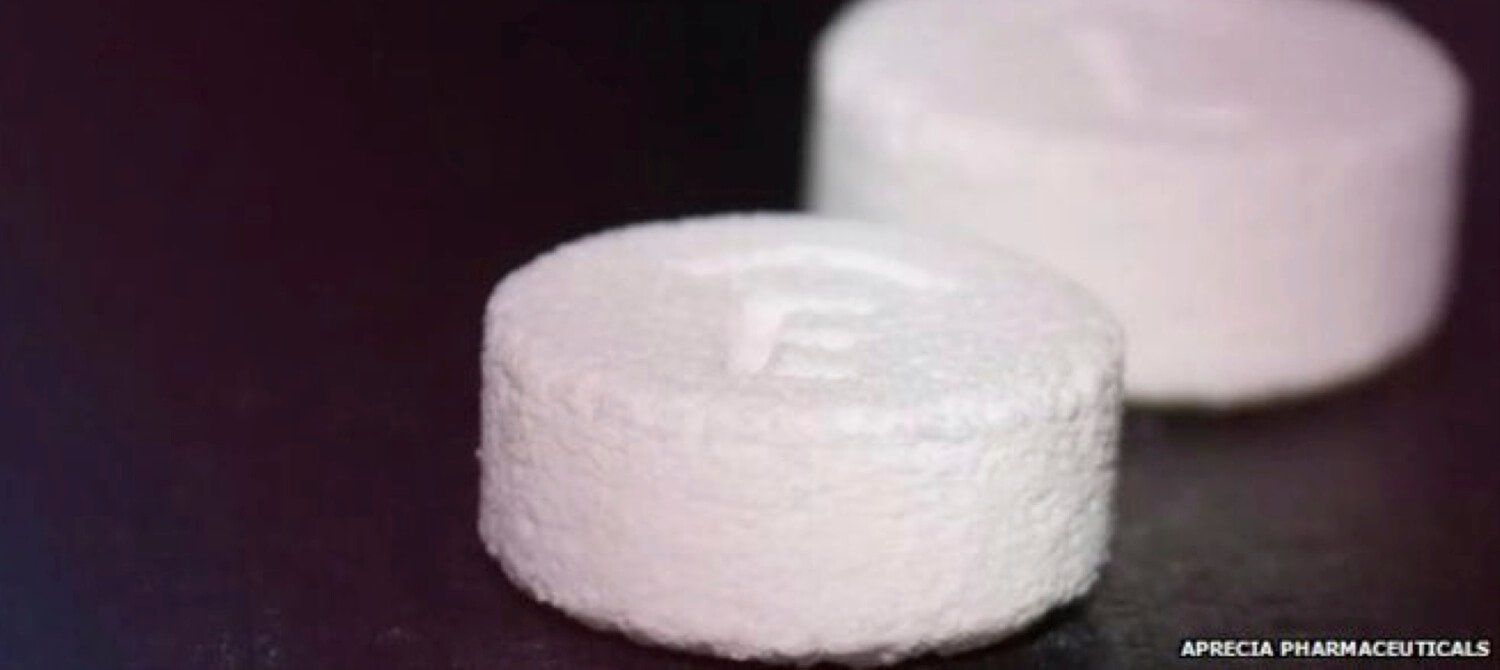
Last week, the FDA approved the first 3D-printed prescription drug, essentially validating the technology as a new heavyweight player in big pharma. “This may be the first truly mass manufactured product made by 3D printing,” said Dr. Michael Cima, a professor at MIT who helped invent the pill-printing technology back in 1997, in an email to Singularity Hub. “It’s revolutionary.”
The printed pill, SPRITAM levetiracetam, is a drug that fights many kinds of epileptic seizures. The brainchild of a little-known Ohio-based company Aprecia, SPRITAM is essentially an old drug ingredient packaged into a brand new, more effective delivery system. Unlike current formulations of the same drug, SPRITAM immediately dissolves upon contact with water and bursts into effect — a property obviously beneficial when trying to curtail sudden-onset seizure episodes.