Feb 1, 2021
Synthetic biology reinvents development
Posted by Quinn Sena in categories: bioengineering, biological, mathematics, physics
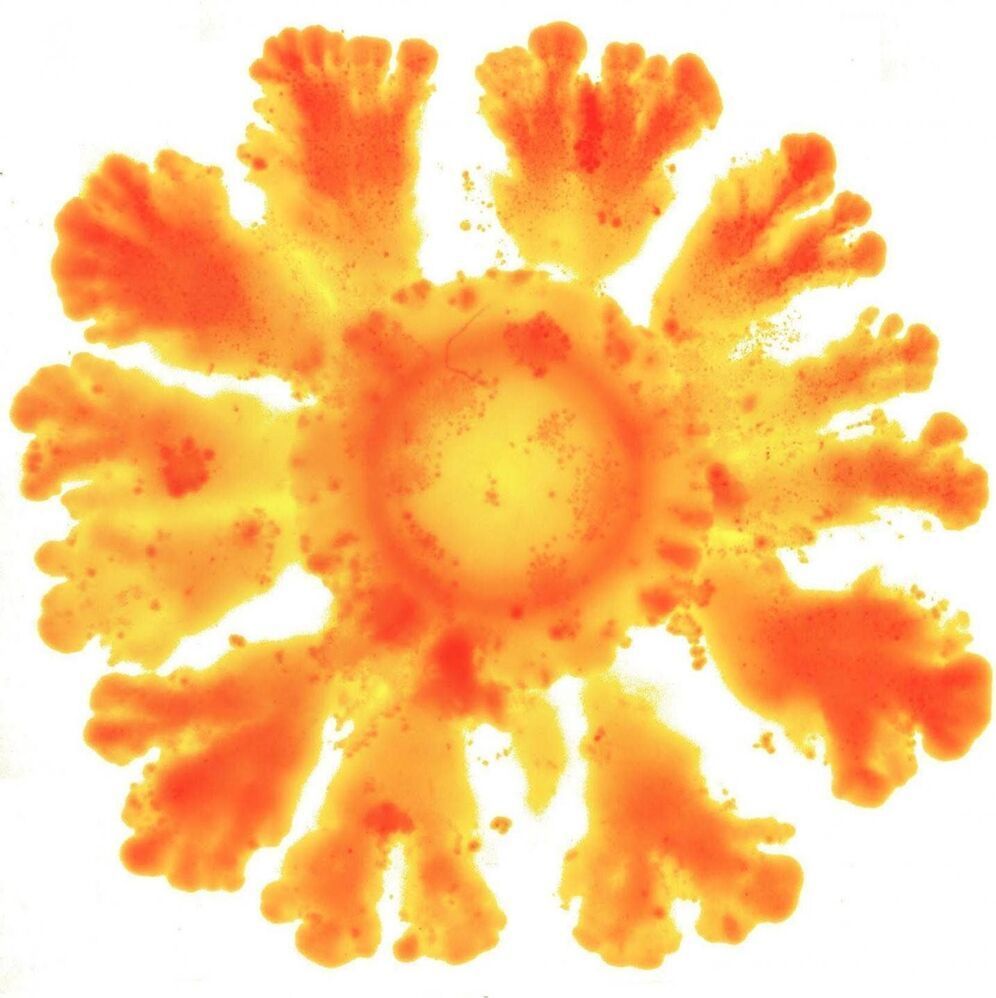
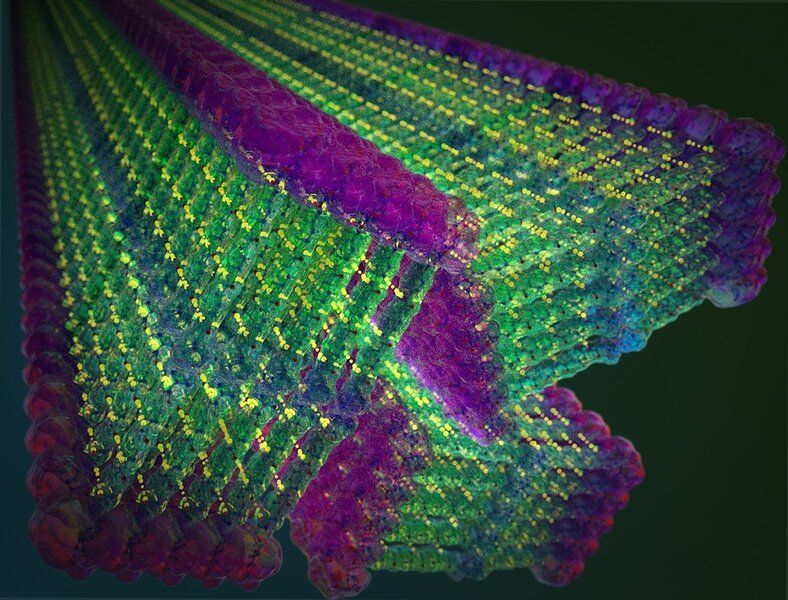
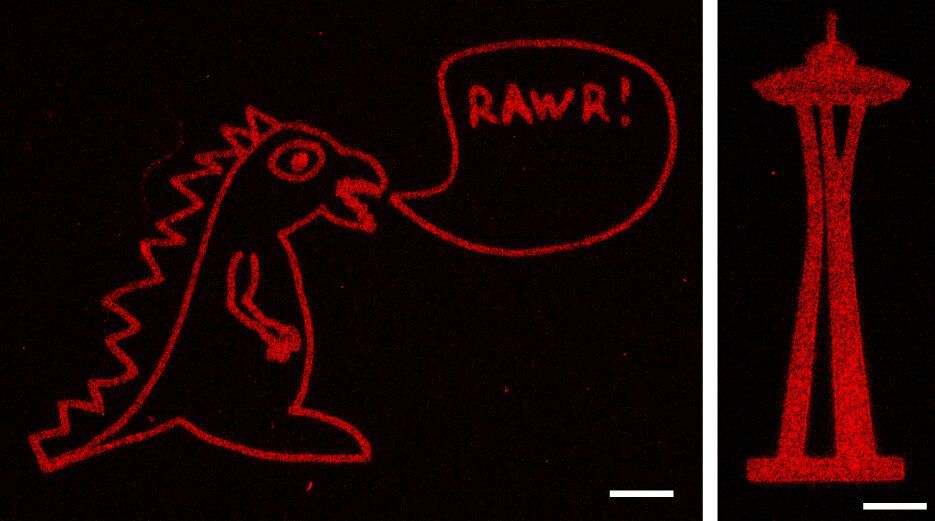
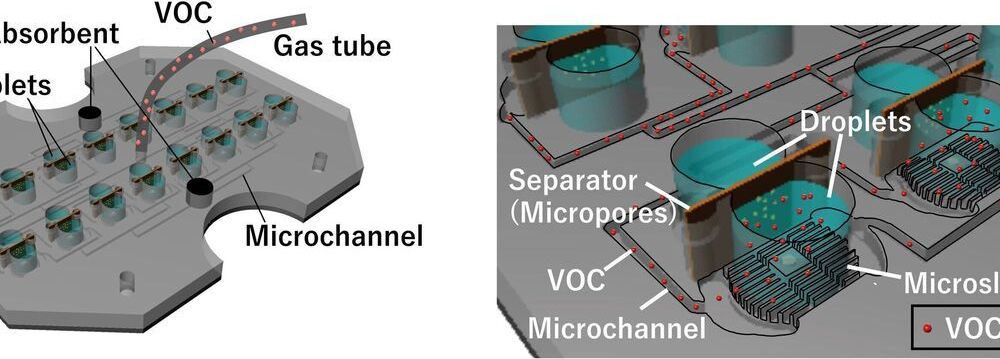
Richard Feynman, one of the most respected physicists of the twentieth century, said “What I cannot create, I do not understand.” Not surprisingly, many physicists and mathematicians have observed fundamental biological processes with the aim of precisely identifying the minimum ingredients that could generate them. One such example are the patterns of nature observed by Alan Turing. The brilliant English mathematician demonstrated in 1952 that it was possible to explain how a completely homogeneous tissue could be used to create a complex embryo, and he did so using one of the simplest, most elegant mathematical models ever written. One of the results of such models is that the symmetry shown by a cell or a tissue can break under a set of conditions.