Archive for the ‘bioengineering’ category: Page 115
Mar 24, 2020
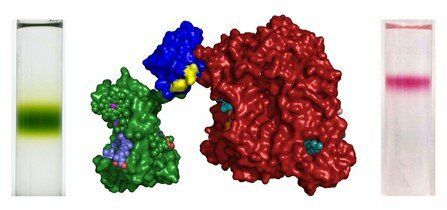
Team develops photosynthetic proteins for expanded solar energy conversion
Posted by Quinn Sena in categories: bioengineering, biological, solar power, sustainability
A team of scientists, led by the University of Bristol, has developed a new photosynthetic protein system enabling an enhanced and more sustainable approach to solar-powered technological devices.
The initiative is part of a broader effort in the field of synthetic biology to use proteins in place of man-made materials which are often scarce, expensive and can be harmful to the environment when the device becomes obsolete.
The aim of the study, published today in Nature Communications, was the development of “chimera” photosynthetic complexes that display poly-chromatic solar energy harvesting.
Mar 22, 2020
Elon Musk: Should Have 1000 Ventilators Next Week, + 250,000 N95 Masks For Hospitals Tomorrow Exclusive
Posted by Genevieve Klien in categories: bioengineering, biotech/medical, Elon Musk, ethics, health, policy, space travel, sustainability

Dr. Ezekiel Emanuel, an American oncologist and bioethicist who is senior fellow at the Center for American Progress as well as Vice Provost for Global Initiatives at the University of Pennsylvania and chair of the Department of Medical Ethics and Health Policy, said on MSNBC on Friday, March 20, that Tesla and SpaceX CEO Elon Musk told him it would probably take 8–10 weeks to get ventilator production started at his factories (he’s working on this at Tesla and SpaceX).
Mar 21, 2020
The new coronavirus was not genetically engineered, study shows
Posted by Quinn Sena in categories: bioengineering, biotech/medical, evolution, genetics
Josie Golding, Ph.D., who is the epidemics lead at the Wellcome Trust, a research charity based in London, United Kingdom, did not participate in the study but comments on its significance.
She says the findings are “crucially important to bring an evidence-based view to the rumors that have been circulating about the origins of the virus (SARS-CoV-2) causing COVID-19.”
“[The authors] conclude that the virus is the product of natural evolution,” Goulding adds, “ending any speculation about deliberate genetic engineering.”
Mar 19, 2020
Here are the stories — in their own words — of five women of synthetic biology
Posted by Genevieve Klien in categories: bioengineering, biotech/medical
Numbers don’t lie, they say. And the numbers show that, as with other life sciences and biotech fields, the number of women in leadership positions in the synthetic biology space is disappointingly low. Last year, I reported that only 14% of the 236 synthetic biology companies I surveyed were led by women. I think most people would agree this is a serious issue — and that something needs to be done about it. But all too often, well-meaning, proactive efforts fizzle out before they have a chance to make a real impact. Why?
I think one of the biggest problems lies in what the numbers can’t show us. The numbers can’t help us understand what it is like, day in and day out, to be a woman in a space where your authority, expertise, and qualifications are constantly questioned. The numbers can’t help us feel the sadness, anger, and frustration facing many women in synthetic biology. The numbers don’t adequately describe what it is really like to be a woman in synthetic biology, so for those that aren’t a woman in synthetic biology, the problem is easily forgotten, or assumed to be taken care of by, who else, the women in synthetic biology.
To put some emotion and empathy behind the numbers — rather than distance and apathy — I recently reached out to several leading women in the synthetic biology space for their stories. In their own, non-sugar coated words, here’s what’s it’s really like to be a woman in synthetic biology. I hope you are as inspired by their stories as I am.
Mar 19, 2020
COVID-19 coronavirus epidemic has a natural origin
Posted by Nicholi Avery in categories: bioengineering, biotech/medical, evolution
I know some have speculated that the Coronavirus was engineered:
An analysis of public genome sequence data from SARS-CoV-2 and related viruses found no evidence that the virus was made in a laboratory or otherwise engineered.
The novel SARS-CoV-2 coronavirus that emerged in the city of Wuhan, China, last year and has since caused a large scale COVID-19 epidemic and spread to more than 70 other countries is the product of natural evolution, according to findings published today in the journal Nature Medicine.
Continue reading “COVID-19 coronavirus epidemic has a natural origin” »
Mar 19, 2020
Scientists program cells to carry out gene-guided construction projects
Posted by Montie Adkins in categories: bioengineering, genetics
Stanford researchers have developed a technique that reprograms cells to use synthetic materials, provided by the scientists, to build artificial structures able to carry out functions inside the body.
“We turned cells into chemical engineers of a sort, that use materials we provide to construct functional polymers that change their behaviors in specific ways,” said Karl Deisseroth, professor of bioengineering and of psychiatry and behavioral sciences, who co-led the work.
In the March 20 edition of Science, the researchers explain how they developed genetically targeted chemical assembly, or GTCA, and used the new method to build artificial structures on mammalian brain cells and on neurons in the tiny worm called C. elegans. The structures were made using two different biocompatible materials, each with a different electronic property. One material was an insulator, the other a conductor.
Mar 18, 2020
New kind of CRISPR technology to target RNA, including RNA viruses like coronavirus
Posted by Quinn Sena in categories: bioengineering, biotech/medical, genetics, robotics/AI
Now, in an important new resource for the scientific community published today in Nature Biotechnology, researchers in the lab of Neville Sanjana, PhD, at the New York Genome Center and New York University have developed a new kind of CRISPR screen technology to target RNA.
The researchers capitalized on a recently characterized CRISPR enzyme called Cas13 that targets RNA instead of DNA. Using Cas13, they engineered an optimized platform for massively-parallel genetic screens at the RNA level in human cells. This screening technology can be used to understand many aspects of RNA regulation and to identify the function of non-coding RNAs, which are RNA molecules that are produced but do not code for proteins.
By targeting thousands of different sites in human RNA transcripts, the researchers developed a machine learning-based predictive model to expedite identification of the most effective Cas13 guide RNAs. The new technology is available to researchers through an interactive website and open-source toolbox to predict guide RNA efficiencies for custom RNA targets and provides pre-designed guide RNAs for all human protein-coding genes.
Mar 15, 2020
The five hottest synthetic biology job markets in the world
Posted by Genevieve Klien in categories: bioengineering, biotech/medical
Although the majority of the synthetic biology market is concentrated in North America and Europe, the synthetic biology landscape is growing worldwide — with some of the fastest growing areas developing outside of the United States. There are several hotspots — formed when innovation at one company or university lab sparks new spinoffs — that synthetic biology followers should pay close attention to in the coming months and years.
The United Kingdom and Ireland
Among non-US hotspots for synthetic biology, the United Kingdom stands out. While most US universities still lack programs in synthetic biology, they are not hard to come by in the UK. Imperial College London, the University of Warwick, Cambridge University, and the University of Edinburgh are all particularly noteworthy for the depth and breadth of synthetic biology research. And, OpenPlant, a joint initiative between the University of Cambridge, John Innes Centre, and the Earlham Institute, is advancing synthetic biology by engineering the next generation of DNA tools for “smart” crop breeding systems.
Mar 14, 2020
Jugaad epitomized: a deep dive into India’s synthetic biology scene
Posted by Genevieve Klien in categories: bioengineering, biotech/medical
Google the word “jugaad,” and you’ll find a plethora of results, from simple dictionary definitions to advice that Western companies should adopt it as part of their practices. Jugaad — a colloquial Hindi, Bengali, and Punjab word — simply means “hack,” and captures the pervasive Indian spirit of finding a low-cost — and sometimes quite resourceful — solution to any problem. If this word doesn’t make one think of entrepreneurship, I don’t know what does.
Indeed, the small-scale biotech facilities scattered all across India, offering products with extremely high adoption rates such as microbial-based biofertilizers, capture the essence of jugaad. In India, finding solutions to the problems at hand is very natural, a way of life, essentially — and any solution, especially an economically sensible one, will be readily adopted. With such a pervasive ideal, India seems like the perfect setting for synthetic biology and biotech-based innovation.