Feb 15, 2019
3D Printed Graphene Aerogel Offers Highest-Ever Capacitance for a Supercapacitor
Posted by Quinn Sena in categories: 3D printing, materials
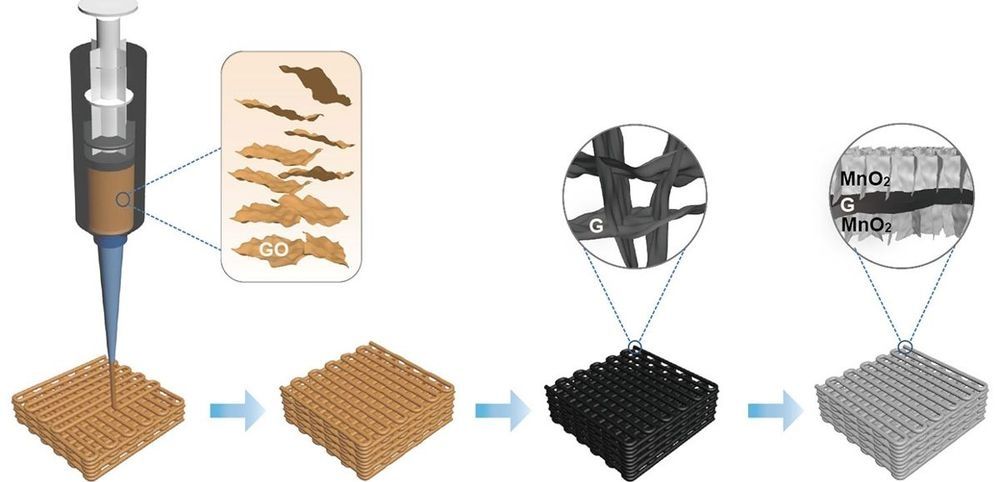
After what has seemed a bit of a lapse in the timeline of their development, graphene-enabled supercapacitors may be poised to make a significant advance. Researchers at the University of California, Santa Cruz, and Lawrence Livermore Laboratory (LLNL) have developed an electrode for supercapacitors made from a graphene-based aerogel. The new supercapacitor component has the highest areal capacitance (electric charge stored per unit of surface area) ever reported for a supercapacitor.
The 3D-printing technique they leveraged to make the graphene electrode may have finally addressed the trade-offs between the gravimetric (weight), areal (surface area), and volumetric (total volume) capacitance of supercapacitor electrodes that were previously thought to be unavoidable.
In previous uses of pure graphene aerogel electrodes with high surface area, volumetric capacitance always suffered. This issue has typically been exacerbated with 3D-printed graphene aerogel electrodes; volumetric capacitance was reduced even further because of the periodic large pores between the printed filaments.